The Earth is experiencing a fever. Global temperatures are on the rise, driven by the ever-increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This phenomenon, known as global warming, is causing a multitude of problems, and one of the most immediate threats is the rise of extreme heat events. According to NOAA’s 2023 Annual Climate Report, the combined land and ocean temperature has increased by an average of 0.11° Fahrenheit (0.06° Celsius) per decade since 1850. The rate of warming has increased to 0.36° F (0.20° C) per decade since 1982.
Heat waves Intensify:
Across the globe, heat waves are becoming more frequent, intense, and longer-lasting. From scorching deserts to bustling metropolises, these scorching periods disrupt daily life, strain infrastructure, and pose serious health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations like older people, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
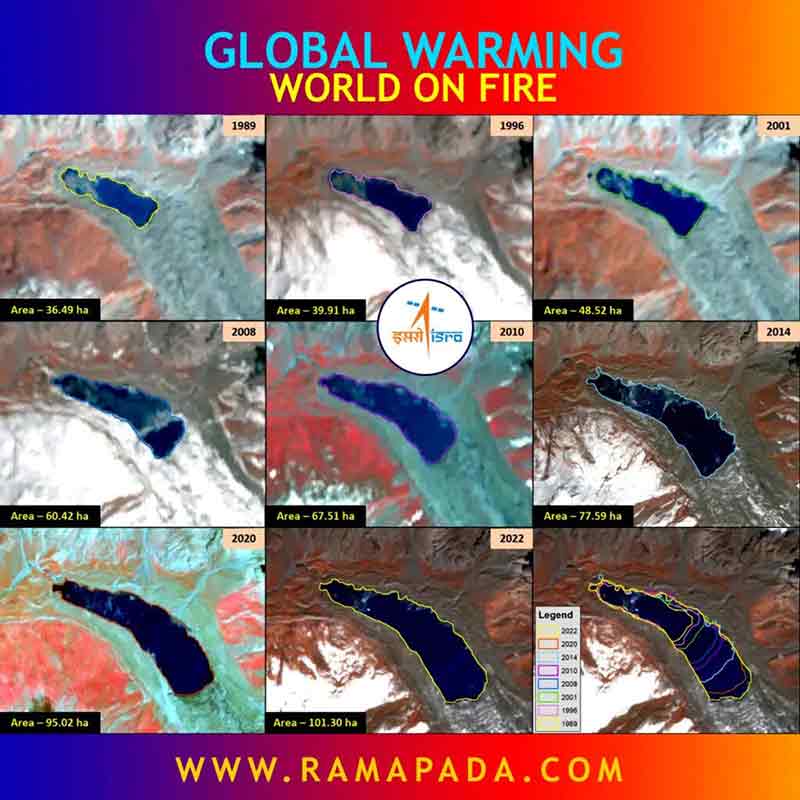
89% of glacial lakes in the Indian Himalayas expanding at an unprecedented rate, reveals ISRO research.
India in the Hot Seat:
India, a nation already grappling with scorching summers, is experiencing the brunt of this rising heat. Heat waves are becoming a regular occurrence, with temperatures exceeding 45 degrees Celsius (113 degrees Fahrenheit) in some regions. These extreme events not only disrupt daily life but also threaten agricultural output, water security, and public health.
Rising Temperatures, Shifting Climate
Average temperatures in India have already risen by 1.94°C (3.5°F) since 1901. This may seem small, but it disrupts weather patterns with far-reaching consequences. Heatwaves, once rare occurrences, are becoming more frequent and severe. In 2022, parts of India and Pakistan saw temperatures exceeding 51°C (124°F).
Monsoon Woes
India’s agricultural sector heavily relies on the annual monsoon season. However, climate change is making monsoons more erratic. There’s a decline in overall rainfall, punctuated by intense downpours that lead to flash floods. This unpredictability creates a double threat: droughts and floods, jeopardizing food security for millions.
Melting Glaciers, Rising Seas
The Himalayas, a vital source of freshwater for India’s rivers, are home to glaciers that are rapidly melting. This not only reduces freshwater availability but also contributes to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities.
Impact on People and Economy
The consequences of global warming are felt across India. Farmers struggle with unpredictable weather patterns, heatwaves reduce labor productivity, and extreme weather events displace communities and damage infrastructure. All this takes a toll on the country’s economy.
Double Trouble:
The situation in India is further exacerbated by factors like rapid urbanization and a lack of green cover in cities. Urban heat islands, where concrete and asphalt absorb and trap heat, can make temperatures feel even higher. This “double whammy” of global warming and urban heat islands creates a dangerous situation for millions of Indians.
Finding Solutions:
Combating this growing threat requires a multi-pronged approach. Here are some key solutions:
- Mitigation: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the root cause of global warming.
- Adaptation: Building resilience to extreme heat events is equally important. India can implement measures like planting trees in cities, using reflective roofing materials, and promoting water conservation to create a cooler urban environment.
- Early Warning Systems: Strengthening early warning systems for heat waves can give people valuable time to prepare and take precautions, potentially saving lives.
- Cooling Centers: Establishing cooling centers in vulnerable areas can provide temporary relief during extreme heat events, especially for those without access to air conditioning.
A Global Responsibility:
- Climate Change Impact:
Hotter weather patterns, attributed to climate change, are becoming more frequent and intense. This puts pressure on the global community to take responsibility for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change effects, and adapting to the changing climate to protect vulnerable communities, ecosystems, and economies. - Heatwaves and Health:
Hot weather, especially extreme heatwaves, can pose significant health risks, particularly to older people, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. In this context, global responsibility would involve efforts to ensure access to cooling centers, promote heat safety measures, and address the root causes of heat-related illnesses, including urban heat islands and inadequate infrastructure. - Environmental Impact:-
Hot weather can exacerbate environmental issues such as droughts, wildfires, and water scarcity, which have global implications for food security, biodiversity, and ecosystem health. Global responsibility entails collaborative efforts to conserve water resources, prevent deforestation, and implement sustainable land management practices to mitigate these impacts.
Conclusion
By working together, implementing these solutions, and prioritizing a sustainable future, we can create a world that is better equipped to handle the increasing heat. While the challenge is daunting, there is still hope. India’s battle against global warming is a story unfolding in real-time. The choices we make today, both locally and internationally, will determine the future of this vast and vibrant country. By transitioning to cleaner energy sources, adapting to changing weather patterns, and working together, we can mitigate the worst effects of climate change and ensure a sustainable future for India.